|
XGC1
|
|
XGC1
|
This module contains the code to evaluate the matrix entries in 2-dimensional linear finite element equations of Helmholtz form -div(alpha grad(X) + beta X = gamma. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| subroutine | helm2delem (alpha, beta, ul, xl, ss, pp, isw, ntor, bfield_coeffs, set_bmat) |
| Evaluates each element's (i.e., triangle's) contributions to the RHS matrix of the Helmholtz equation \(\nabla\cdot(\alpha\nabla_\perp \phi)+\beta\phi\). The matrix entries of the RHS matrix can then be obtained by summing the contributions of all elements that belong to a mesh vertex. Thus, this routine returns a 3x3 matrix \(A_{ij}\), where \(i\) and \(j\) are the indices of the three vertices of the triangular element. More... | |
| subroutine | diff2delem (D, pinch_v, xl, geo_factors, ss, mass_flag, pinch_flag, indirect_pinch_flag) |
| Evaluates each element's (i.e., triangle's) contributions to the RHS matrix of the radial diffusion equation equation \(\nabla(D_{ij}\cdot\nabla n)\). The matrix \(D_{ij}\) is \(D_{ij}=D(\psi,\theta) \hat{\boldsymbol{\psi}} \bigotimes \hat{\boldsymbol{\psi}}\). The matrix entries of the RHS matrix can then be obtained by summing the contributions of all elements that belong to a mesh vertex. Thus, this routine returns a 3x3 matrix \(A_{ij}\), where \(i\) and \(j\) are the indices of the three vertices of the triangular element. More... | |
| subroutine | bdotgradelem (ul, xl, bb, pp, area) |
| Evaluates \(\boldsymbol{B}\cdot\nabla\) in the poloidal plane, i.e., \(B_R \partial/\partial R + B_Z \partial/\partial Z\) using triangular linear finite elements. More... | |
| subroutine | new_thfx2d (alpha, ul, shp, gradpot, pot, dd) |
| Evaulates the value and derivative of a function in linear finite element space based on the three triangle basis functions and their derivatives (shp). The routine also returns the "material tensor" (dd), which in case of XGC's Poisson equation is \(A_{ij}\) in \(\nabla(A_{ij}\cdot\nabla_\perp\) with \(A_{ij}\) being a diagonal 2x2 matrix (R and Z) with the polarization \(\alpha\) on the diagonal. More... | |
| subroutine | new_tint2d (l, lint, el) |
| Sets up Gauss points for 1 or 3-point integration rule on a triangle The Gauss points are given by their barycentric coordinates in the triangle el(1:3,:), and their weight el(4,:). The weight is either 1 for 1-point integration or 1/3 for 3-point integration. More... | |
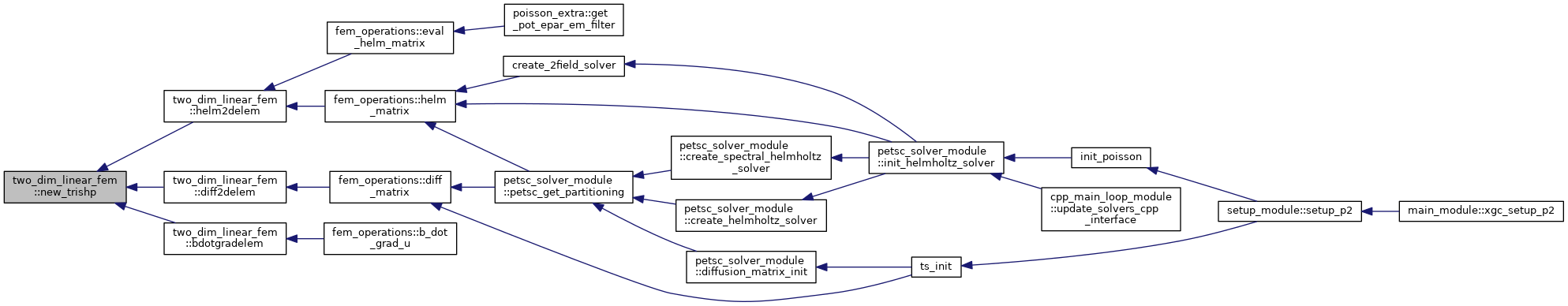
| subroutine | new_trishp (el, xl, xsj, shp) |
| Calculates the linear basis functions in a triangular finite element. More... | |
This module contains the code to evaluate the matrix entries in 2-dimensional linear finite element equations of Helmholtz form -div(alpha grad(X) + beta X = gamma.
| subroutine two_dim_linear_fem::bdotgradelem | ( | real(kind=8), dimension(3), intent(in) | ul, |
| real(kind=8), dimension(2,3), intent(in) | xl, | ||
| real(kind=8), dimension(3,2), intent(in) | bb, | ||
| real(kind=8), dimension(3), intent(out) | pp, | ||
| real(kind=8), dimension(3), intent(out) | area | ||
| ) |
Evaluates \(\boldsymbol{B}\cdot\nabla\) in the poloidal plane, i.e., \(B_R \partial/\partial R + B_Z \partial/\partial Z\) using triangular linear finite elements.
| [in] | ul | Function value \(f\) in \(\boldsymbol{B}\cdot\nabla f\) on the triangle vertices |
| [in] | xl | R and Z coordinates of the triangle vertices of the current element |
| [in] | bb | R and Z components of the magnetic field on each triangle vertex |
| [out] | pp | "In-plane" component of \(\boldsymbol{B}\cdot\nabla f\) |
| [out] | area | Fractions of triangle area attributed to the triangle vertices |
| subroutine two_dim_linear_fem::diff2delem | ( | real (kind=8), intent(in) | D, |
| real (kind=8), intent(in) | pinch_v, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(2,3), intent(in) | xl, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(3), intent(in) | geo_factors, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(3,3), intent(out) | ss, | ||
| logical, intent(in) | mass_flag, | ||
| logical, intent(in) | pinch_flag, | ||
| logical, intent(in) | indirect_pinch_flag | ||
| ) |
Evaluates each element's (i.e., triangle's) contributions to the RHS matrix of the radial diffusion equation equation \(\nabla(D_{ij}\cdot\nabla n)\). The matrix \(D_{ij}\) is \(D_{ij}=D(\psi,\theta) \hat{\boldsymbol{\psi}} \bigotimes \hat{\boldsymbol{\psi}}\). The matrix entries of the RHS matrix can then be obtained by summing the contributions of all elements that belong to a mesh vertex. Thus, this routine returns a 3x3 matrix \(A_{ij}\), where \(i\) and \(j\) are the indices of the three vertices of the triangular element.
| [in] | D | Radial diffusion coefficient, real(8) |
| [in] | pinch_v | Particle pinch velocity, real(8) |
| [in] | geo_factors | Geometry related coefficients (R,dpsi/dR,dpsi/dZ,|grad(psi)|,<|grad(psi)|>, real(8) |
| [in] | xl | Coordinates of triangle vertices, real(8) |
| [out] | ss | 3x3 matrix \(A_{ij}\) with the contributions of the element to the RHS matrix entries in the radial diffusion equation |
| [in] | mass_flag | F –> diffusion matrix (or pinch), T –> mass matrix |
| [in] | pinch_flag | F –> diffusion or mass matrix, T –> particle pinch |
| [in] | indirect_pinch_flag | F –> diffusion/mass_matrix/pinch, T –> particle pinch contribution in momentum and density equation |
| subroutine two_dim_linear_fem::helm2delem | ( | real (kind=8), intent(in) | alpha, |
| real (kind=8), intent(in) | beta, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(3), intent(in) | ul, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(2,3), intent(in) | xl, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(3,3), intent(out) | ss, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(3), intent(out) | pp, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | isw, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | ntor, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(6), intent(in) | bfield_coeffs, | ||
| logical, intent(in) | set_bmat | ||
| ) |
Evaluates each element's (i.e., triangle's) contributions to the RHS matrix of the Helmholtz equation \(\nabla\cdot(\alpha\nabla_\perp \phi)+\beta\phi\). The matrix entries of the RHS matrix can then be obtained by summing the contributions of all elements that belong to a mesh vertex. Thus, this routine returns a 3x3 matrix \(A_{ij}\), where \(i\) and \(j\) are the indices of the three vertices of the triangular element.
| [in] | alpha | Polarization factor \(n_0 m_i/B^2\), real(8) |
| [in] | beta | Density to temperature ratio \(n_0/T_e\), real(8) |
| [in] | ul | Value of a function f on the vertices when calculating grad(f) or f on a Gauss point, real(8) |
| [in] | xl | Coordinates of triangle vertices, real(8) |
| [out] | ss | 3x3 matrix \(A_{ij}\) with the contributions of the element to the RHS matrix entries in the Helmholtz equation (used only with isw==1) |
| [out] | pp | Result of \(nabla\cdot(\alpha\nabla_\perp\phi)+\beta\phi\) (used only with isw==2; requires input of ul) |
| [in] | isw | Mode of operation: isw==1 –> calculate matrix elements, isw==2 –> evaluate LHS of Helmholtz equation for given phi |
| [in] | ntor | Toroidal mode number (for toroidally spectral solver) |
| [in] | bfield_coeffs | Ratios of different combinations of the components of the magnetic field to the squared total field: (1) \(1-B_R^2/B^2\) (2) \(1-B_Z^2/B^2\) (3) \(1-(B_\varphi B^\varphi)_/B^2\) (4) \(B_R B_Z/B^2\) (5) \(B_R B^\varphi/B^2\) (6) \(B_Z B^\varphi/B^2\) |
| [in] | set_bmat | If false, set up diagonal block of the polarization matrix, else the off-diagonal block (toroidally spectral solver only) |
| subroutine two_dim_linear_fem::new_thfx2d | ( | real (kind=8), intent(in) | alpha, |
| real (kind=8), dimension(3), intent(in) | ul, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(4,*), intent(in) | shp, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(2), intent(out) | gradpot, | ||
| real (kind=8), intent(out) | pot, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(2,2), intent(out) | dd | ||
| ) |
Evaulates the value and derivative of a function in linear finite element space based on the three triangle basis functions and their derivatives (shp). The routine also returns the "material tensor" (dd), which in case of XGC's Poisson equation is \(A_{ij}\) in \(\nabla(A_{ij}\cdot\nabla_\perp\) with \(A_{ij}\) being a diagonal 2x2 matrix (R and Z) with the polarization \(\alpha\) on the diagonal.
| [in] | alpha | Polarization coefficient \(n_0 m_i/B^2\), real(8) |
| [in] | ul | Values of the function to be evaluated on the triangle vertices, real(8) |
| [in] | shp | Linear triangle basis functions and their derivatives, real(8) |
| [out] | gradpot | Gradient of the function to be evaluated, real(8) |
| [out] | pot | Value of the function to be evaluated at a Gauss point (specified by barycentric weights in shp), real (8) |
| [out] | dd | "Material tensor" [[alpha,0],[0,alpha]], real(8) |
| subroutine two_dim_linear_fem::new_tint2d | ( | integer, intent(in) | l, |
| integer, intent(out) | lint, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(4,*), intent(out) | el | ||
| ) |
Sets up Gauss points for 1 or 3-point integration rule on a triangle The Gauss points are given by their barycentric coordinates in the triangle el(1:3,:), and their weight el(4,:). The weight is either 1 for 1-point integration or 1/3 for 3-point integration.
| [in] | l | Number of Gauss points; 1 for 1-point and -3 for 3-point integration, integer |
| [out] | lint | Number of Gauss points (output); -1 if error, integer |
| [out] | el | Baricentric coordinates and weights of Gauss points |
| subroutine two_dim_linear_fem::new_trishp | ( | real (kind=8), dimension(3), intent(in) | el, |
| real (kind=8), dimension(2,*), intent(in) | xl, | ||
| real (kind=8), intent(out) | xsj, | ||
| real (kind=8), dimension(4,*), intent(out) | shp | ||
| ) |
Calculates the linear basis functions in a triangular finite element.
| [in] | el | Barycentric coordinates of Gauss point used for integration, real(8) |
| [in] | xl | (R,Z) coordinates of the triangle vertices, real(8) |
| [out] | xsj | Triangle area, real(8) |
| [out] | shp | Derivatives of the 3 shape functions, real(8) |
 1.8.5
1.8.5